Japan’s 2-year authorities bond yield surged to 1% on December 1, its highest since 2008. Financial institution of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda signaled a doable rate of interest hike on the December 18-19 financial coverage assembly, sending ripples by world monetary markets.
This improvement might mark the top of three many years of ultra-low rates of interest that fueled the yen carry commerce. As borrowing prices rise and the yen strengthens, world markets now brace for important deleveraging throughout asset courses.
Bond Yields Climb as Charge Hike Expectations Develop
Japan’s bond market moved sharply following Ueda’s current statements. The two-year word yield rose by one foundation level to 1%. Longer-dated bonds additionally noticed features: five-year yields rose about 4 foundation factors to 1.35%, and 10-year yields climbed to 1.845%, in accordance with Bloomberg information.
Throughout buying and selling, 10-year authorities bond yields reached 1.850%, their highest degree since June 2008. This 17-year excessive highlights market perception that the BOJ will tighten coverage quickly. The shift in yields underscores the speedy change in investor sentiment on the central financial institution’s subsequent transfer.
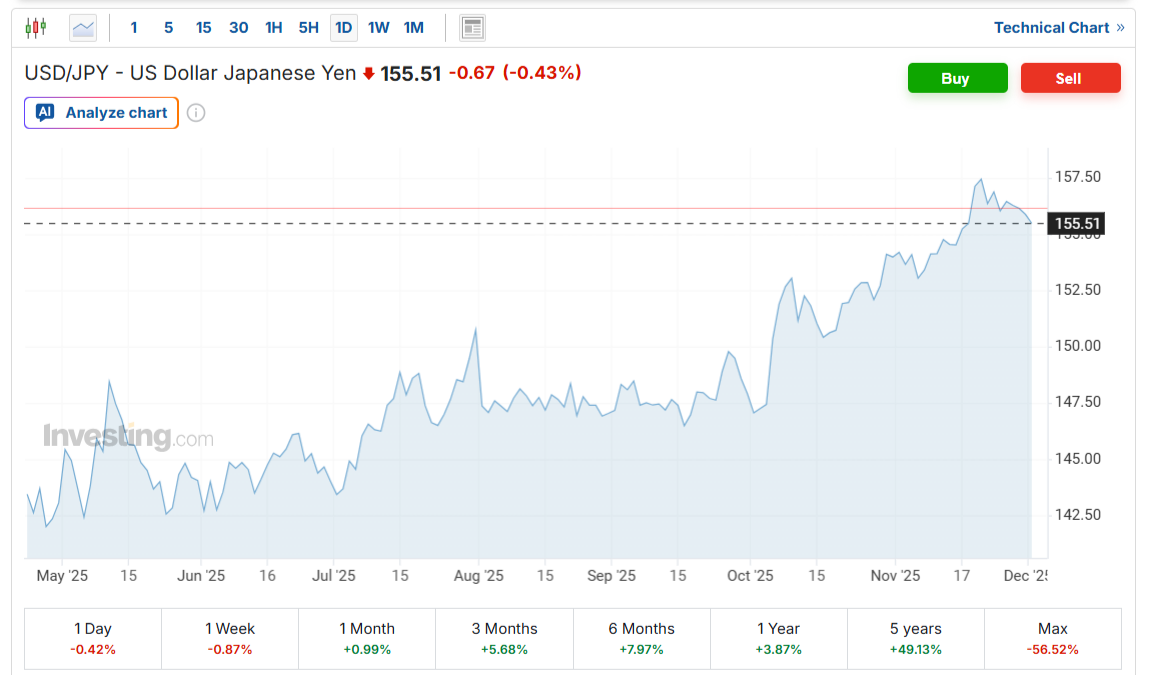
Supply: investing.com
Markets responded rapidly. The yen gained as a lot as 0.4% towards the greenback, buying and selling at 155.49 on December 1. This reversal from November’s ranges displays rising expectations of upper Japanese rates of interest, that are making yen property newly engaging.
At a enterprise assembly in Nagoya, Ueda acknowledged that lowered uncertainty across the US financial system and tariffs bolstered confidence in Japan’s financial and value outlook. He reaffirmed that well timed fee modifications are key for monetary stability and assembly the two% inflation goal.
Inflation and Fiscal Coverage Drive Shift Towards Tightening
The federal government’s expansionary fiscal coverage has added to inflation pressures, constructing a case for financial tightening. Yen depreciation has lifted import costs, fueling shopper inflation and elevating questions in regards to the sustainability of value stability. Governor Ueda highlighted the rising affect of a weaker yen on import prices and warned that expectations might have an effect on core inflation.
Market forecasts now counsel the BOJ’s coverage fee might attain 1.4% following three 25-basis-point hikes from the present 0.5% fee. Primarily based on In a single day Listed Swap charges and 1-year ahead charges, expectations are clearly rising. Katsutoshi Inatome of Mitsui Sumitomo Belief stated {that a} hike in December would push future fee estimates even greater.
The BOJ faces a cautious steadiness. Whereas lifting charges tackles inflation and helps the forex, it might disrupt monetary flows which have relied on low cost Japanese funding. Ueda emphasised that any hike can be measured in an accommodative method, not as a pointy break. He added that Japanese coverage has revived a system the place each wages and costs can rise reasonably.
World Markets React as Yen Carry Commerce Nears Finish
The doable unwinding of the yen carry commerce marks a major change for world finance. For 30 years, traders borrowed yen at low charges to hunt greater returns elsewhere, supporting asset costs from US shares to rising market bonds. This supplied leverage that fueled many market rallies.
As Japanese charges climb, the economics of the carry commerce shift. Debtors who locked in 1% funding with a secure yen now face reimbursement at 3% and a forex that has appreciated by 10%. This raises the efficient borrowing value to round 13%, making such trades far much less engaging. The August 2024 flash crash previewed the turmoil that may happen when carry commerce positions unwind rapidly.
“For 30 years, the Yen Carry Commerce backed world conceitedness — zero charges… free leverage… faux progress… complete economies constructed on borrowed time and borrowed cash. Now Japan has reversed the swap. Charges climbed. Yen strengthened. And the world’s favorite ATM simply became a debt-collector.” – AlgoBoffin
The Nikkei 225 fell 1.88% as deleveraging started, and analysts warn that this might begin a cycle of compelled asset gross sales. When low cost yen financing vanishes, markets should depend on basic power as an alternative of leverage. The ripples stretch past Japan, impacting monetary hubs like Wall Road and Shanghai that benefited from yen-driven liquidity.
Cryptocurrency markets are particularly susceptible to tighter world liquidity. Bitcoin and different digital property reply sharply to modifications in funding. Sometimes, danger property take in the primary wave of volatility when liquidity dries up, probably inflicting swings in crypto valuations.
These **three charts collectively (Japan 10Y + Silver + Bitcoin)** are telling one of many **clearest macro tales of our lifetime**.
## **1️⃣ Japan 10-Yr Yield (The Starting of the Finish of “Free Cash”)**
For 30+ years, Japan saved rates of interest close to **zero**.
This created the… pic.twitter.com/JBIOu3SrwS— ajay patel (@ajaycan) December 1, 2025
Some analysts argue that this transition exposes underlying market dynamics which have been masked by years of free financial coverage. As liquidity tightens and charges normalize, asset costs could also be judged extra on intrinsic worth than on low cost financing. This shift may gain advantage some commodities and laborious property, however problem progress sectors that flourished with ultra-low charges.
The approaching weeks are pivotal because the BOJ considers its December determination. Markets are set for tightening, however the actual tempo is unknown. Whether or not Japan chooses gradual or sharper fee will increase will form how rapidly and severely world deleveraging unfolds. The period of free Japanese cash appears to be ending, ushering in a interval of upper volatility and higher scrutiny of market fundamentals worldwide.
The put up Yen Carry Crypto Buying and selling Over? Japan Alerts Charge Hike appeared first on BeInCrypto.









